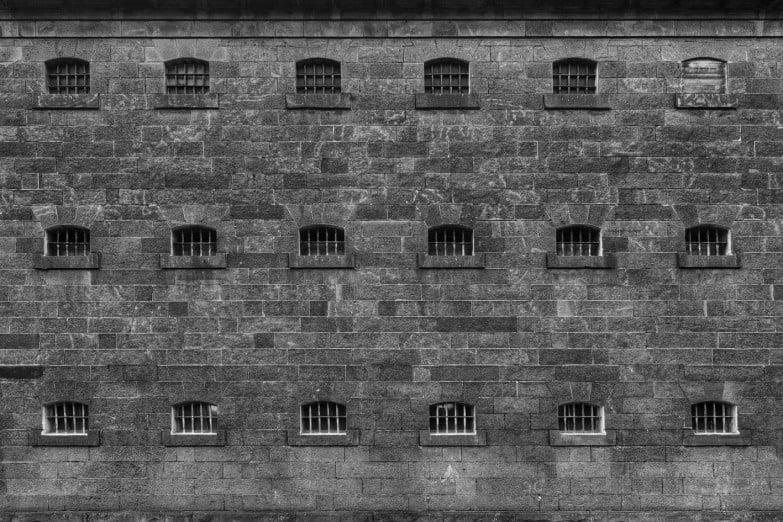
| Unit 1 | Legal Foundations | The role of individuals, laws and the legal system in achieving social cohesion and protecting the rights of individuals | Consider if the Gaol worked as a way to deter people from a life of crime. |
| Unit 1, 2 | | The principles of justice: fairness, equality and access | Consider the questions – was the Gaol a fair place? Did it achieve justice? |
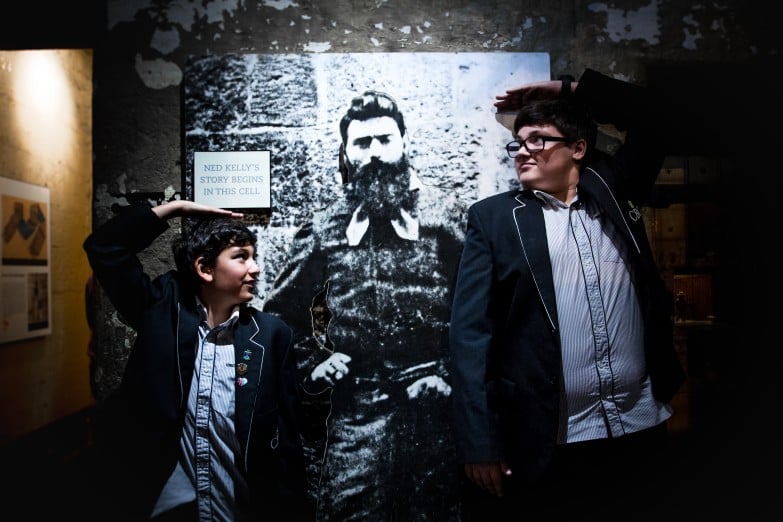
| Unit 1 | The Presumption of Innocence | Types of crime such as crimes against the person and crimes against property | Study the case of Ned Kelly as an example of crimes against the person. |
| Unit 2 | Sanctions | Types of sanctions such as fines, community correction orders and imprisonment | Learn about the many different sanctions within the walls of the Gaol including corporal punishment, solitary confinement, hard labour, and capital punishment. |
| Unit 2, 3 | | The purposes of sanctions: punishment, deterrence, denunciation, protection and rehabilitation | Understand the rationale behind the Gaol; deterrence and rehabilitation and assess whether it achieved these aims. |
| Unit 3 | The Victorian Criminal Justice System | Factors considered in sentencing, including aggravating factors, mitigating factors, guilty pleas and victim impact statements | Learn that historically, legal proceedings were not as fair as they are today, and this resulted in many more people likely to end up at the Gaol due to their gender, race, sexual orientation, political beliefs, religious beliefs, and social status. |
| Unit 4 | The People, The Parliament and The Courts | The ability and means by which individuals can influence law reform including through petitions, demonstrations and the use of the courts | Learn about the many protests that took place outside the walls for clemency in cases such as Ned Kelly and females sentenced to death like Frances Knorr, Emma Williams and Elizabeth Scott. |
| SOCIOLOGY | | |
| Unit 2 | Deviance | Deviance as a relative concept and the relationship between norms (social codes) and deviance | Discuss society in Melbourne in the 1800s, learning about crimes of desperation such as vagrancy which could earn you 12 months in prison. Learning about the 1890s economic depression in Melbourne and how that affected the prison population. |
| | A range of factors that lead people to commit crimes, including poverty, addiction, abuse, and rebellion. | Students will discuss the types of people likely to be imprisoned, paying particular attention to the poor and mistreated. |
| | The impact of moral panic on individuals and groups considered deviant. | Learn about the many women who were imprisoned at the Gaol and their supposed deviance compared to how women 'should' behave. |
| Crime and Punishment | Australian data related to crime rates, including age, gender, socioeconomic status and ethnicity | Link the societal changes and political climate with the demographics within prison. |
| | The sociological concept of punishment, including the rationale and aims of punishment: retribution, deterrence, rehabilitation and societal protection | Learn about the many different punishments within the walls of the Gaol including corporal punishment, solitary confinement, hard labour and capital punishment. |